Our Specialization
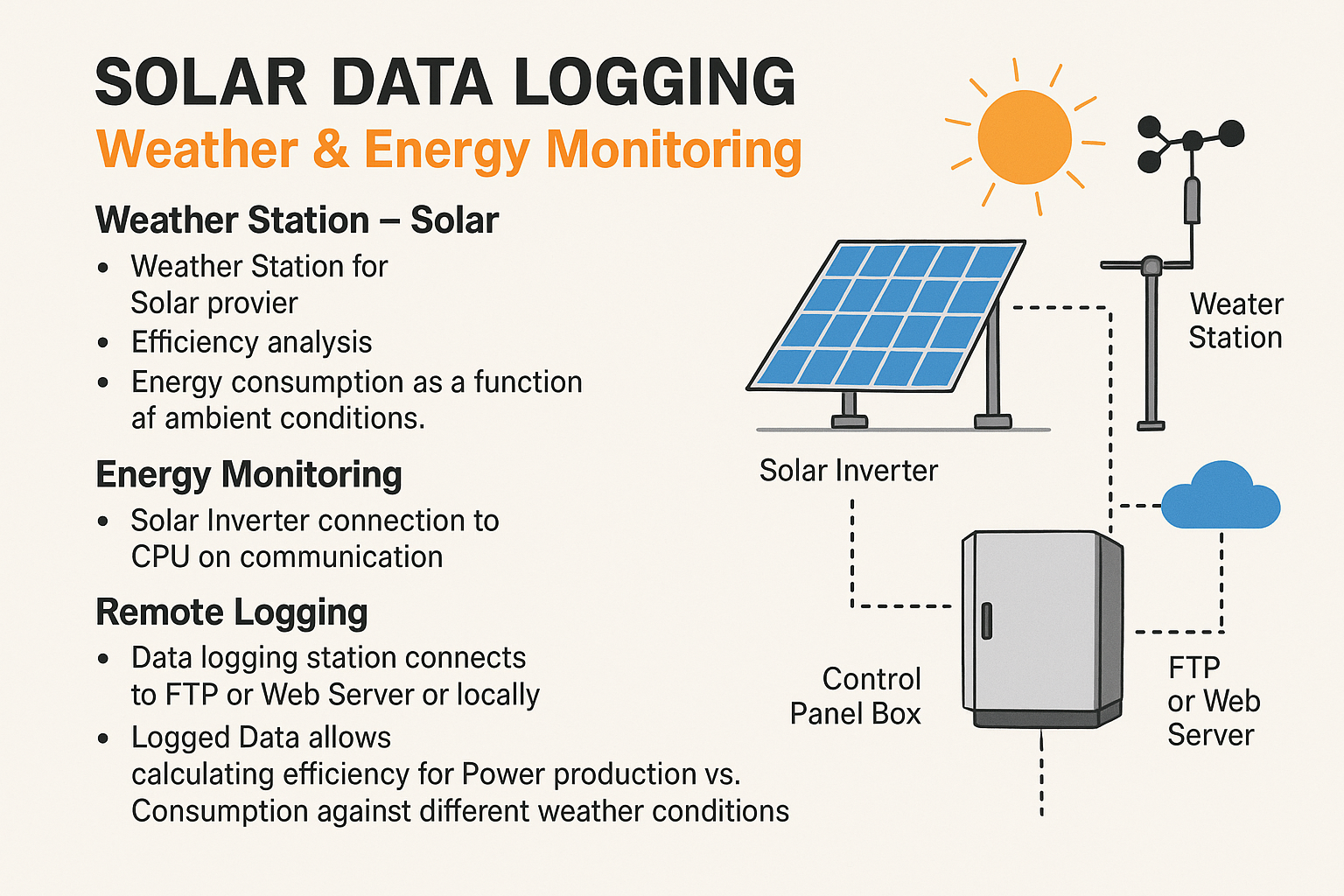
Solar Data Logging System
The Solar Data Logging System is designed to enhance monitoring and efficiency analysis of solar power plants. A weather station plays a key role by recording critical environmental parameters such as solar radiation, wind speed, ambient temperature, and module temperature. This data helps in conducting solar site surveys, evaluating system performance, and analyzing energy consumption in relation to changing weather conditions. The solar inverter, when connected to the CPU, provides real-time information about the power generated along with other relevant data for monitoring. Through remote logging, the system stores data locally, on FTP, or web servers, enabling detailed calculations of power production versus consumption under different climatic scenarios. The entire setup is supported with durable IP65/IP67-rated control panel boxes suitable for both ground mounting and rooftop installations, ensuring reliable and long-term operation.
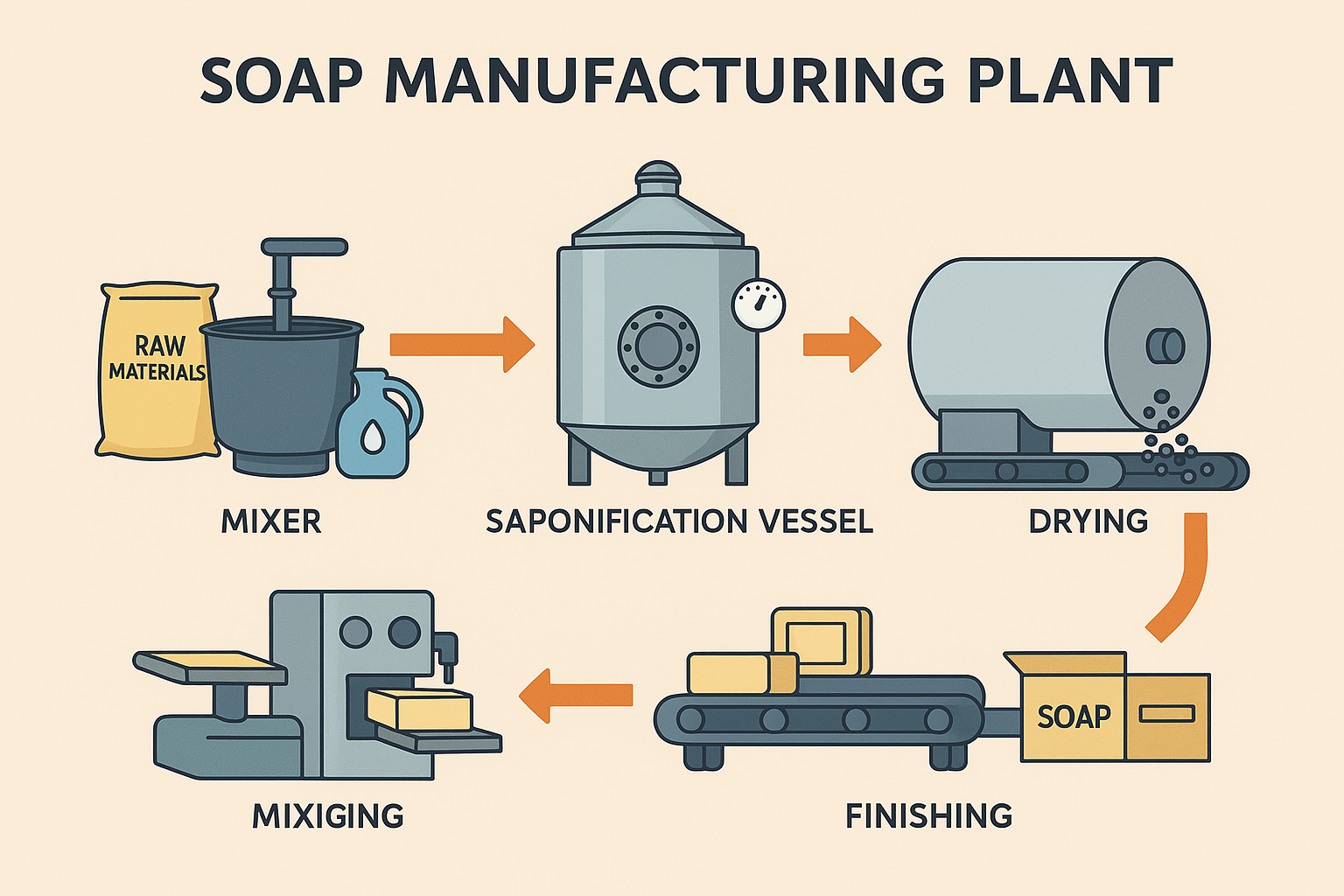
Soap Manufacturing Plant
The Soap Manufacturing Plant document highlights the setup and operation of a production facility designed for efficient soap making. The plant integrates processes such as mixing raw materials, saponification, drying, and final product finishing. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining proper temperature, pressure, and chemical ratios to ensure consistent product quality. Modern soap plants often include automated machinery for cutting, stamping, and packaging, which enhances productivity and reduces manual labor. Additionally, the plant layout is structured to optimize workflow, minimize wastage, and ensure safety standards. Overall, such a facility provides a reliable system for producing high-quality soaps on both small and large scales .
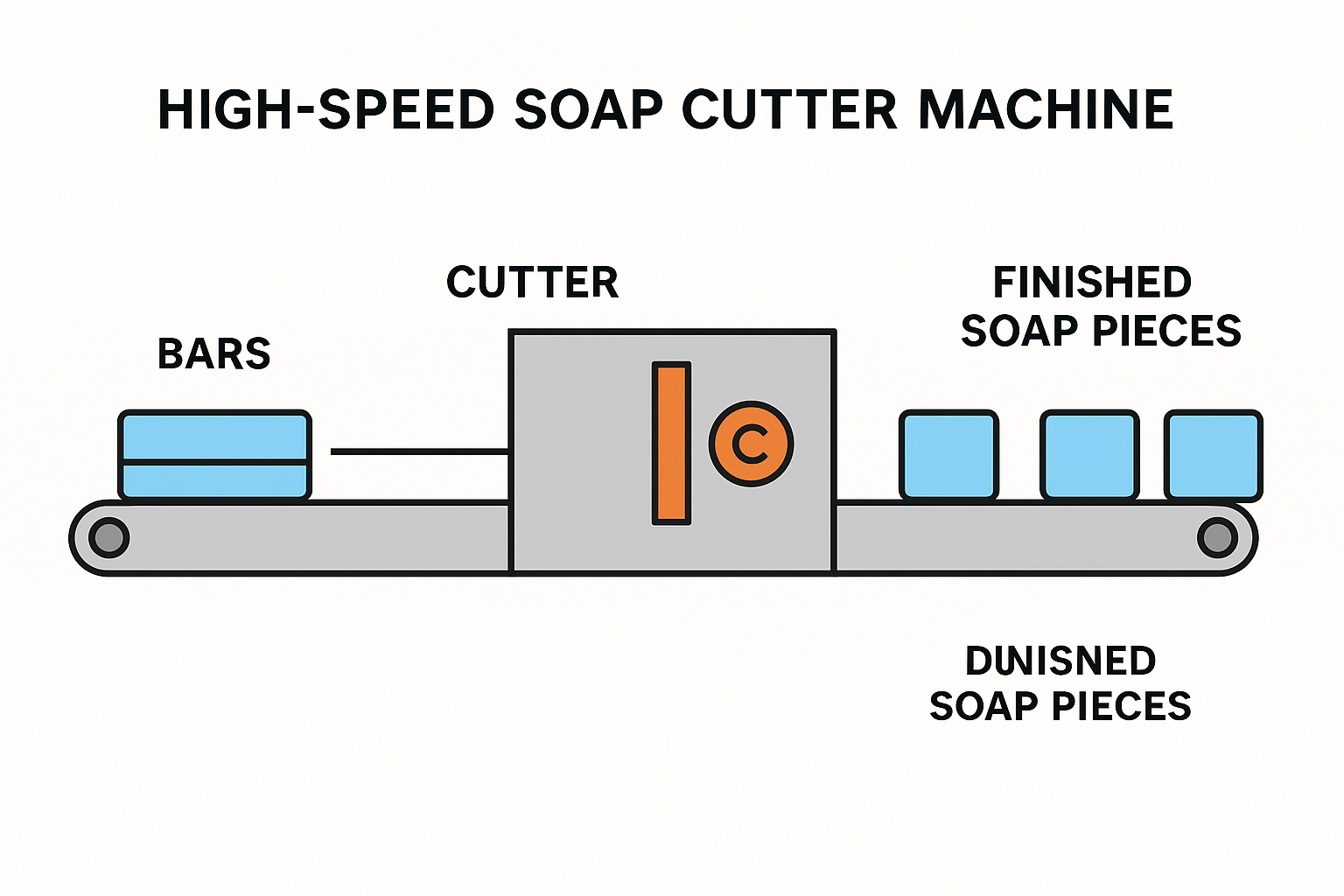
Automatic Soap Cutting Machine
The High-Speed Soap Cutter Machine is a robust and intelligent system designed for efficient soap cutting operations with line speeds up to 300 cuts per minute. It supports both straight and stamping cuts through a double-servo, encoder-based mechanism, ensuring precision and continuous feed. The cutter offers dual cutting options, intelligent power on/off, automatic synchronization with plodder extrusion speed, and foolproof operation with alarm monitoring and single-button reset. It can handle various bar specifications, ranging from small (20×10×25 mm) to large (50×60×240 mm), delivering consistent performance with line speeds up to 480 mm/min. The machine is suitable for both toilet and laundry soap production, providing features like auto-centering of stamping, durable construction, low maintenance design, and reliable after-sales support. With a total weight of approximately 450 kg, 2.0 kW power setup, and 400V AC 3-phase input, this cutter ensures superior performance, durability, and efficiency, backed by a 2-year warranty.
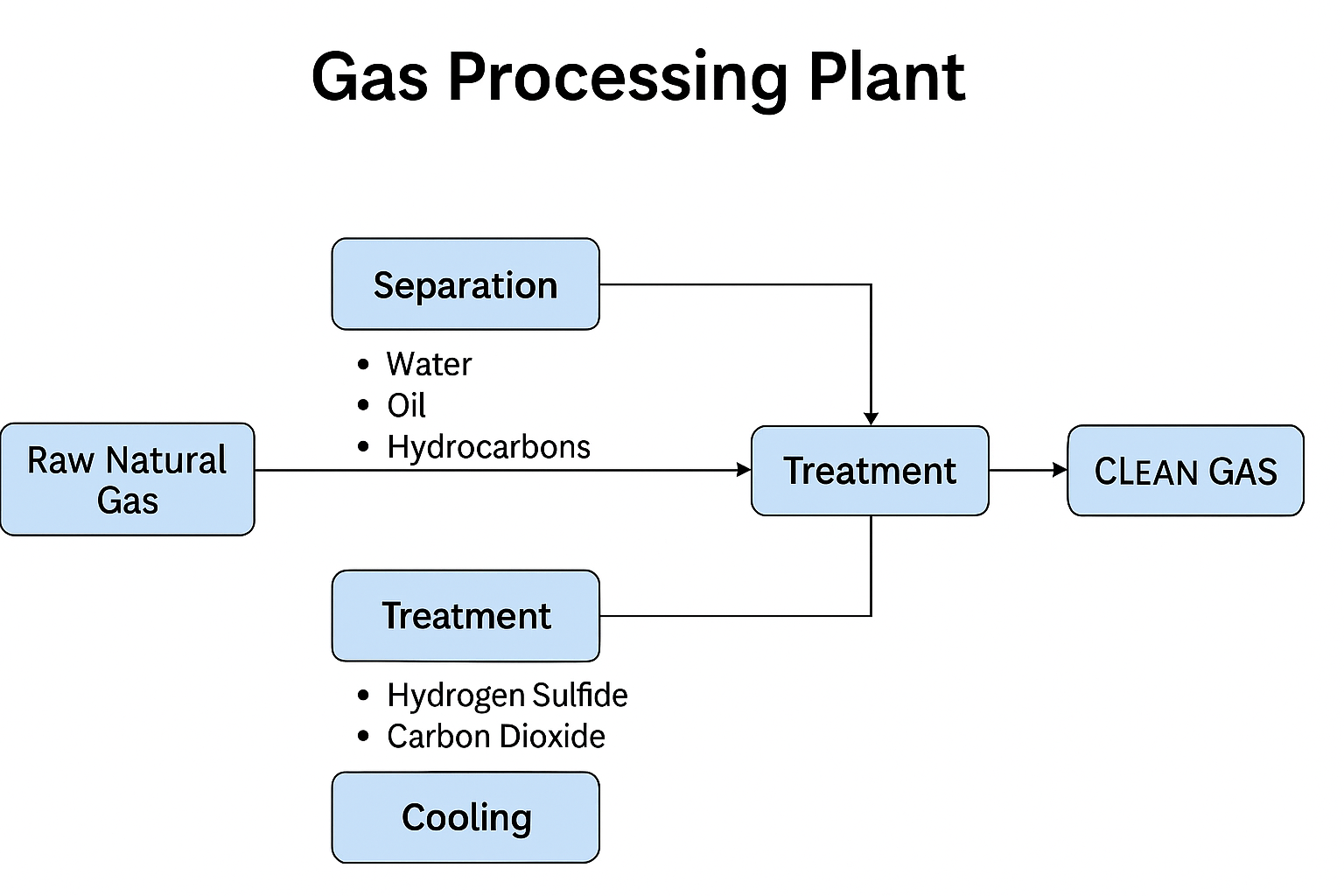
Gas Processing Plant
The Gas Processing Plant is an industrial facility designed to refine raw natural gas into usable and marketable fuel. The process begins with the separation of impurities such as water, oil, and heavier hydrocarbons, followed by treatment to remove toxic gases like hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide. The plant employs key operations including compression, cooling, dehydration, fractionation, and in some cases liquefaction, to ensure purity and efficiency. Modern gas plants are equipped with automated safety systems, optimized layouts, and energy-efficient technologies to maintain continuous operation while complying with environmental standards. The final output is clean natural gas, which is then distributed for industrial, commercial, and domestic applications, making the plant a critical component of the energy supply chain.
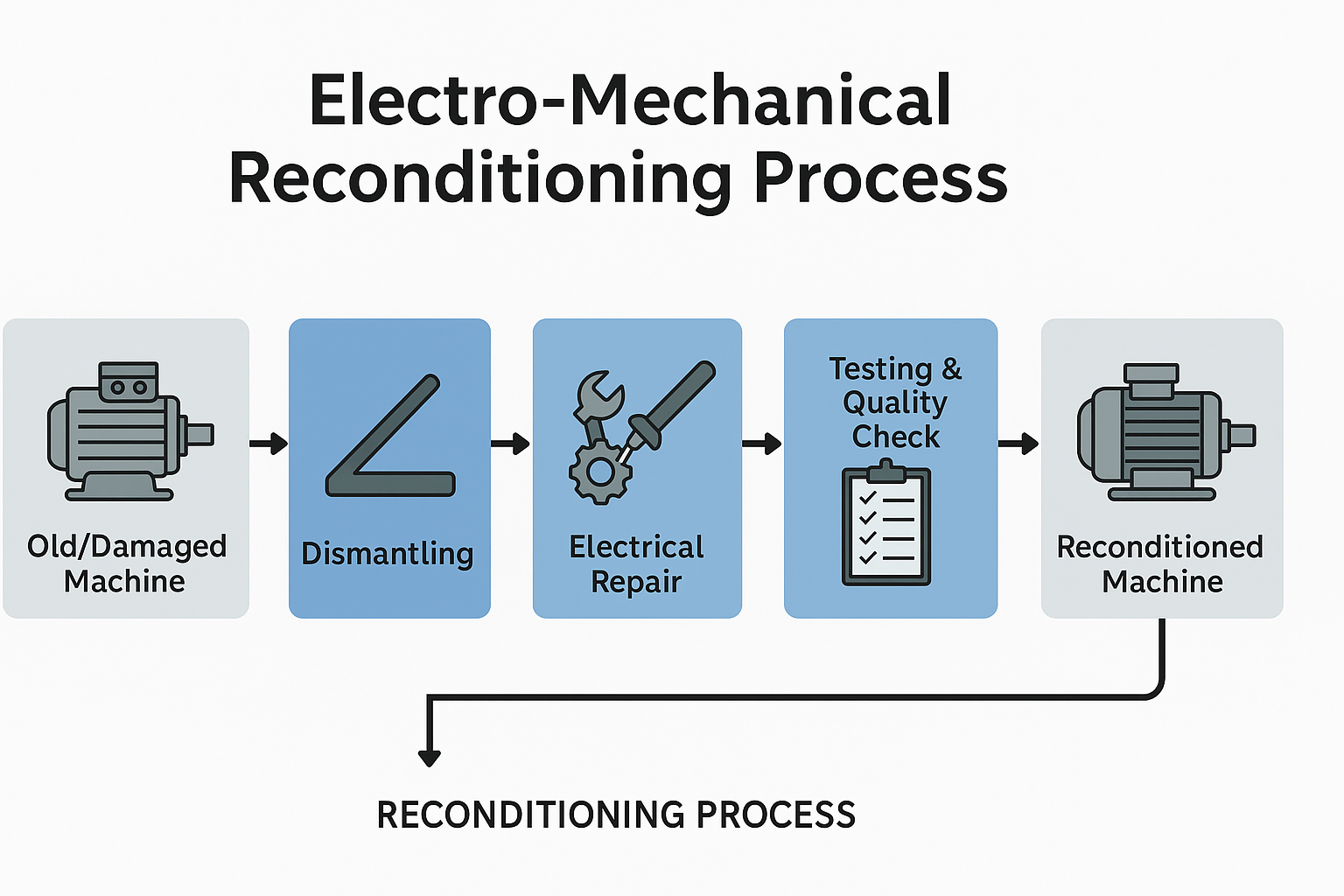
Reconditioning (Electro-Mechanical)
The Electro-Mechanical Reconditioning Process refers to restoring worn-out or damaged machines and equipment back to their original working condition. This involves a systematic overhaul of both electrical and mechanical components. On the mechanical side, processes include dismantling, cleaning, inspection, machining, replacement of worn parts, alignment, and lubrication. On the electrical side, activities involve rewinding motors, replacing insulation, testing control panels, repairing sensors, and upgrading wiring or electronics as needed. The objective is to improve efficiency, extend the equipment’s life, reduce breakdowns, and ensure safe, reliable performance. Modern reconditioning also integrates testing under load conditions and quality checks to certify that the reconditioned equipment meets operational standards.
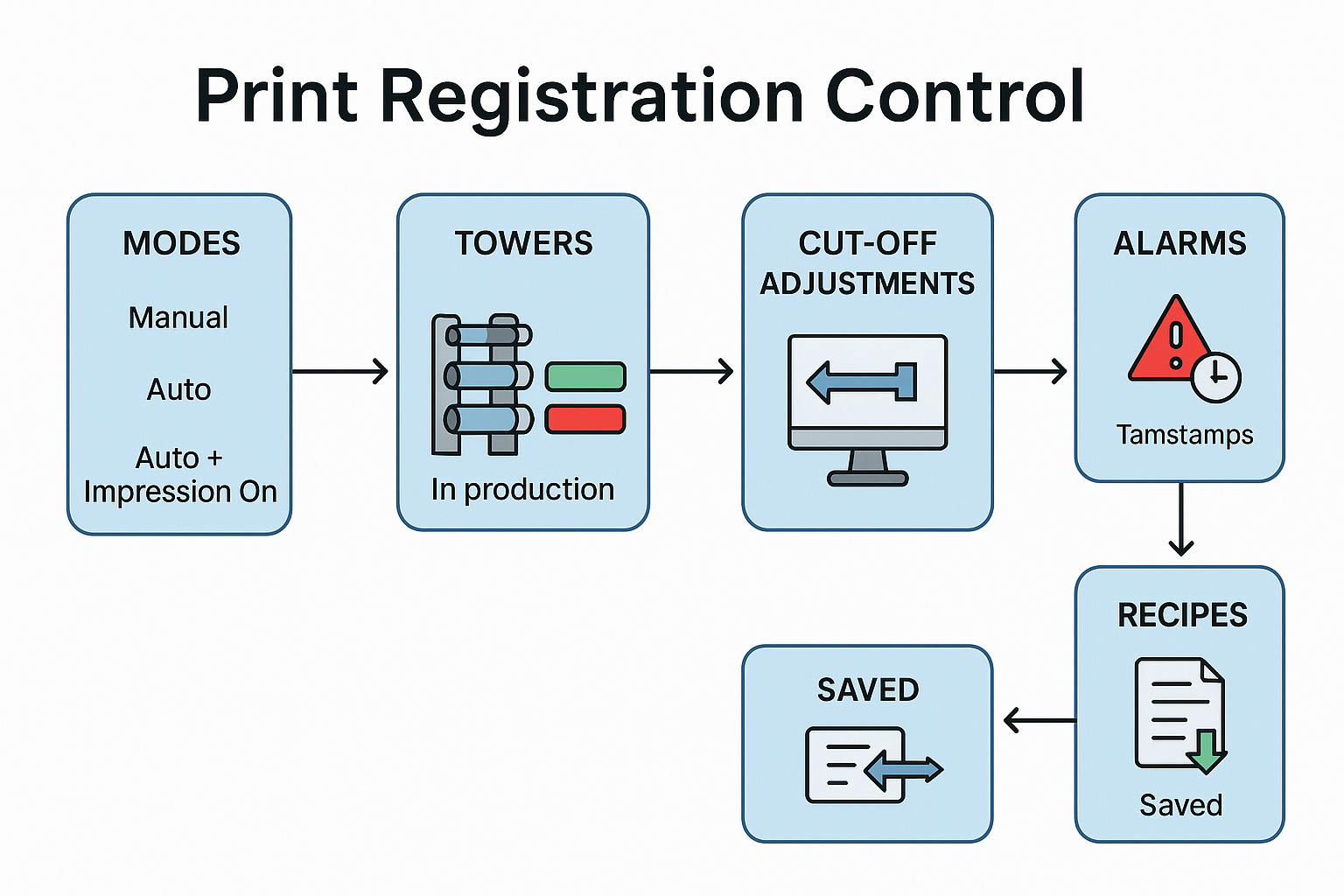
Print Registration Control System
The Print Registration Control System ensures accurate alignment and synchronization in printing operations. It operates in three modes: Manual, Auto, and Auto + Impression On, which can be controlled via the HMI (Human Machine Interface). The system allows monitoring of the Manroland printing towers, showing whether each tower is in production (green) or out of production (red). It uses cameras to capture registration marks, displaying status through color indicators, and provides graphical representation of registration for both top and bottom sides of the towers. Operators can switch between main, tower, alarm, and recipe screens to monitor performance, adjust reference values, or correct cut-off positions. Both manual controls (for moving motors left, right, up, and down) and auto controls are available for precise registration adjustments. Additionally, alarms with timestamps, recipe saving for cut-off and registration, and automatic saving of corrected values enhance system reliability, efficiency, and ease of operatio
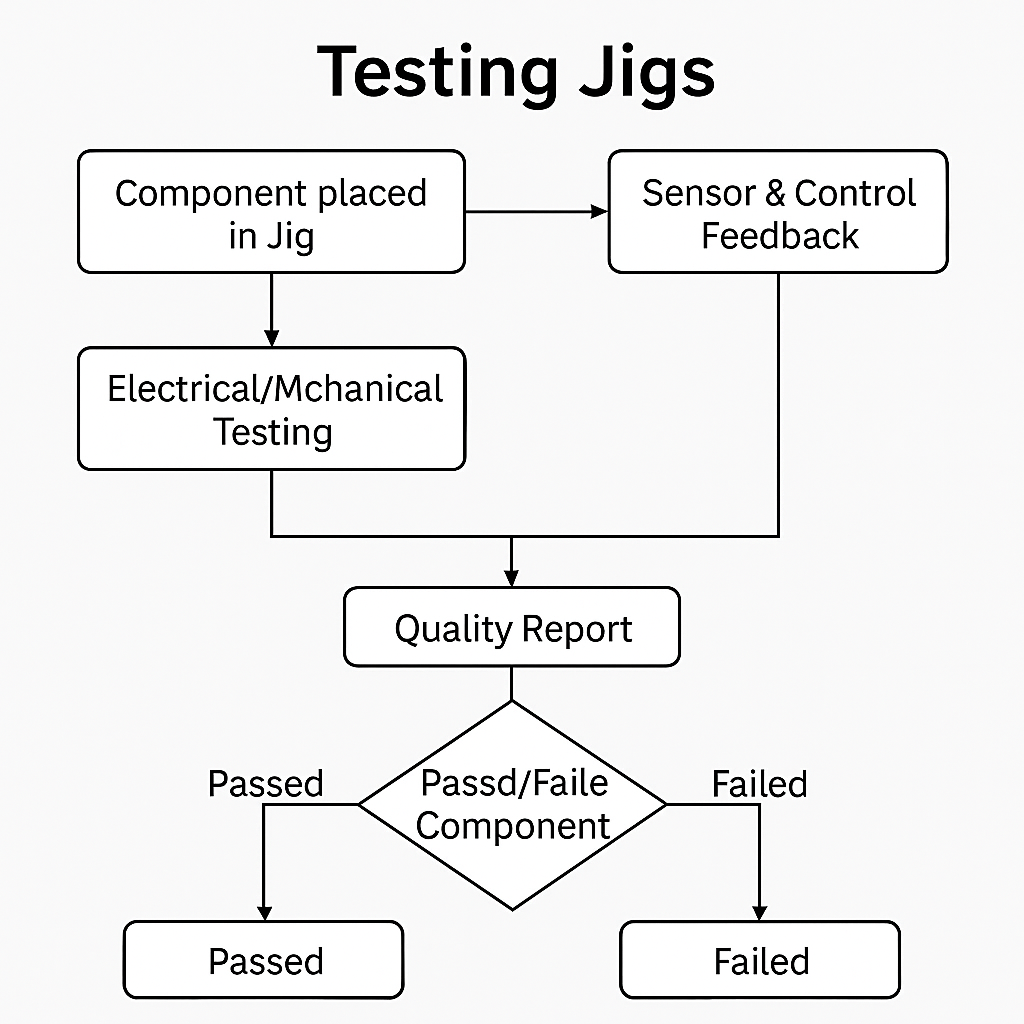
Testing Jigs System
The Testing Jigs System is designed to evaluate and validate the performance of electro-mechanical or electronic components during manufacturing and reconditioning. A jig provides a controlled setup where parts, assemblies, or printed circuit boards (PCBs) can be securely mounted for accurate testing. These systems typically include electrical connections, sensors, actuators, and automated control interfaces to simulate real-world operating conditions. Testing jigs help in detecting defects, verifying dimensions, ensuring alignment, and checking electrical continuity or signal integrity. They are also integrated with monitoring software for recording test results and generating quality reports. By standardizing the testing process, jigs improve accuracy, reduce manual errors, enhance productivity, and ensure that only reliable, high-quality components move forward in production.
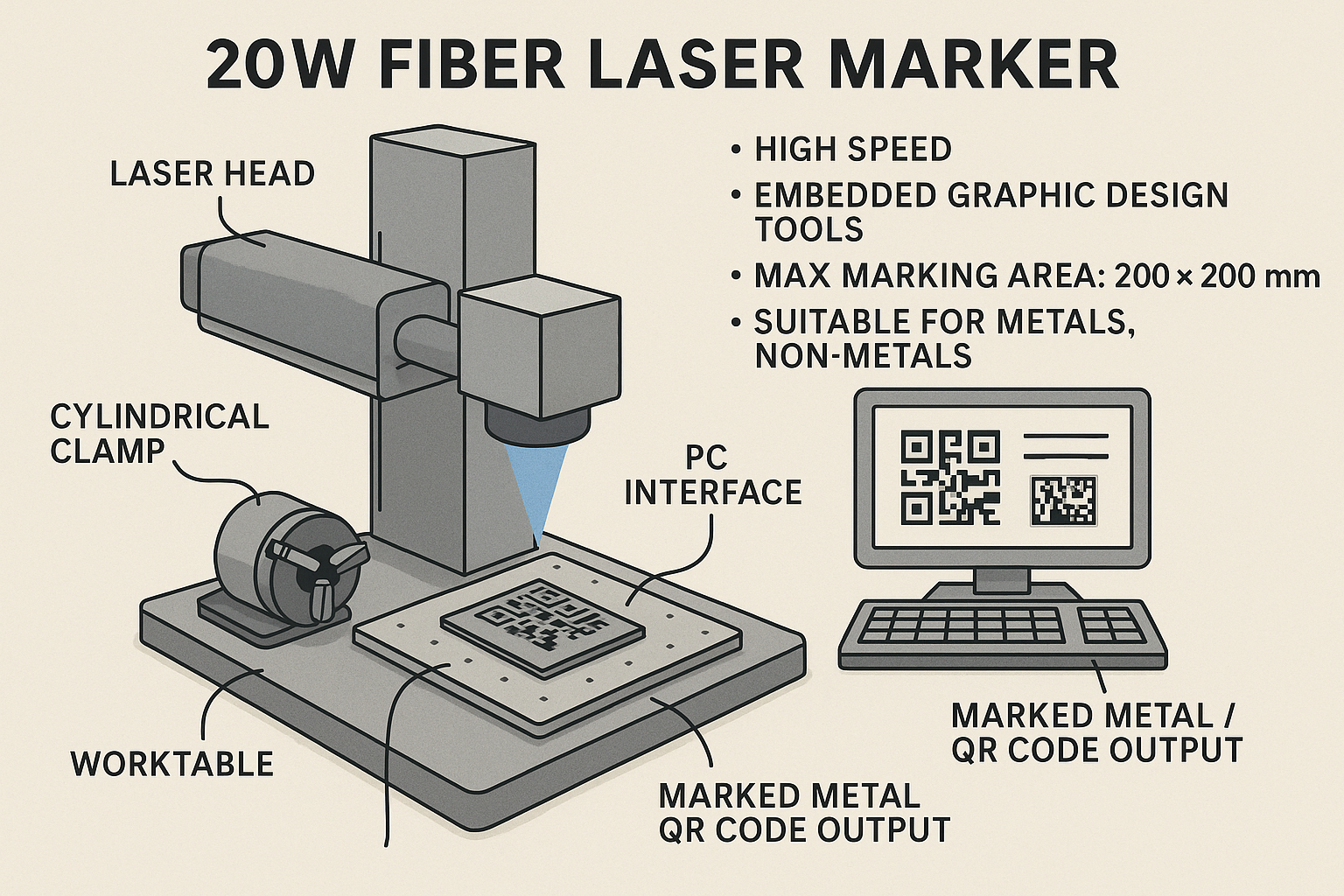
Laser marking Machines
The 20W Fiber Laser Marker is a high-performance machine designed for precision marking on metals and non-metals. It features stable laser power with air-cooled, maintenance-free operation, and supports multiple formats (PLT, BMP, DST) through a user-friendly interface. The system includes embedded graphic design tools, enabling marking of shapes, text, curves, serial numbers, barcodes, and QR codes at speeds up to 9,000 mm/s. With a maximum marking area of 200×200 mm and a detachable CNC rotary clamp for cylindrical objects, it ensures flexibility for diverse applications. The laser produces extremely fine markings, with a minimum line width of 0.01 mm on stainless steel. Key specifications include a 20W fiber laser (1064 nm), worktable size of 250×310 mm, height range of 100 mm, and power supply of 220V AC, 800W. Compact in size (750×210×500 mm), the system integrates with a standard PC setup for control. It comes with a 12-month warranty from site acceptance or 13 months from shipping, ensuring reliability and quality compliance